ARTHRITIS AND INFLAMMATION
Reversing Crohn's, Colitis, and Gut Issues and their Connection to Arthritis and Inflammation
WHAT IS ARTHRITIS?
Arthritis is inflammation of a joint(s). Inflammation is known as the body’s attempt to protect itself through its attempts to remove foreign toxic substances and start the healing process. Your body’s inflammatory response is triggered when tissues are injured by bacteria, trauma, toxins, heat, or any other cause. Although inflammation helps heal wounds, too much inflammation, and inflammation lasting for long periods of time, is harmful to the body. Inflammation can be aggravated by lifestyle habits.
Many of us make the mistake of assuming that arthritis is something that develops as we age and that nothing can be done about it. Since May is Arthritis Awareness Month, we thought it would be a good time to talk about a very common but impairing chronic illness that can be prevented, improved, or even reversed with healthy lifestyle changes.
Sometimes the signs of a chronic illness can be easy to miss. Our lives often whisk us away and distract us from what’s happening with our bodies. We can be experiencing chronic inflammation long before we actually start to feel it and take notice. We all experience different kinds of inflammation for various reasons at any given time. However, if you’re asking yourself whether it’s arthritis, you may be onto something.
How do you know if you are experiencing inflammation? Well, inflammation can be as overt as a swollen knee. It can also happen inside our bodies to a much less noticeable extent, building up over time and becoming a serious problem. Chronic or excess inflammation causes most chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, stroke, liver problems, cancer, dementia, fibromyalgia, and autoimmune disease like thyroid disorder, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 52.5 million people report having been diagnosed with some form of arthritis by their doctor. Arthritis may be caused by an underlying disease, infection, or a genetic defect. Arthritis may cause chronic pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints and can impair a person’s ability to perform regular daily tasks. It is more common among adults aged 65 years or older, but people of all ages (including children) can be affected by arthritis.
When younger people experience joint pain, they hardly ever consider the possibility that it could be a symptom of arthritis. That's why it's important to increase awareness about the importance of lifelong joint health. Taking steps early in life to protect your joints can help prevent further pain and future permanent damage.
Two Types Of Inflammation:
Acute Inflammation
Acute Inflammation begins fast and lasts for a few days to possibly a few weeks. It can become severe quickly. Some examples of acute inflammation are the common cold, the flu, bronchitis, headache, or joint pain. A person may experience pain, immobility, being flushed, or swollen.
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic Inflammation lasts for several months to years. It occurs from chronic exposure to a low-intensity irritant/toxin or an auto-immune response to an allergen. Allergies, arthritis, heart disease, thyroid disorder, diabetes, and most cancers are linked to chronic inflammation.
COMMON TYPES OF ARTHRITIS
There are over 200 different kinds of arthritis and related conditions. Some common forms of arthritis include:
Osteoarthritis: the most common type. It is a degenerative “wear-and-tear” joint disease where pain and swelling stem from the progressive loss of cartilage in the joints. It is considered a normal symptom of aging and can also result from previous damage to the joints.
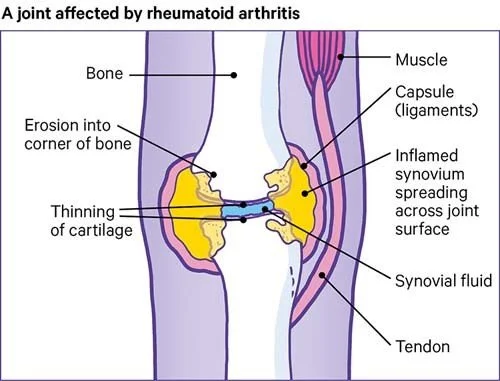
Rheumatoid arthritis: the second most common type of arthritis. It is characterized by inflammation, swelling, fatigue, and pain in the hands (especially the knuckles), wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, and feet. This type of arthritis affects people’s abilities to function more severely, but on the bright side, diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis early can help reduce the impact of the disease on your daily quality of life.
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: It come in multiple forms and affects young children. Diagnosing this type of arthritis early will give your child a better chance to adapt, form healthy habits, and learn how to manage symptoms successfully to reduce the impact it has in their daily life.
ARTHRITIS SYMPTOMS
Early signs of arthritis may be mistaken as vague ghost pains or some sort of injury, strain, or overuse of joints. You may feel tenderness in joints and experience some temporary loss in function. Symptoms can vary depending on what type of arthritis it is. Common symptoms of arthritis include:
Chronic pain
Decreased range of motion in the affected region (joints)
Redness of the joint
Swelling of the joint
Joint tenderness
Joint warmth
Limping
Locking of the joint
Stiffness in the joints
Weakness in the joints
HOW TO PREVENT AND IMPROVE ARTHRITIS SYMPTOMS
The best way to prevent or help resolve inflammation is to listen to your body and pay attention to what increases or reduces your body’s inflammatory response. Making changes to your lifestyle one step at a time will make a huge difference.
GUARANTEED RESULTS
Work with the nation’s top integrative functional medicine physician to uncover the root causes of your symptoms and guided effectively how on to transform your illness into wellness. Dr. Bhandari refuses to accept the status quo commonly accepted in conventional medicine and revert to prescribing immunosuppressive drugs loaded with dangerous side effects when there may be more effective and safer solutions.